Investing in stocks is a common way to grow money over time. When it comes to stock investing, there are lots of strategies you can adapt. Each has its own risks and rewards. An important one is to learn about different types of stocks.
Two of the main stock categories are growth stocks and value stocks. These have distinct features and appeal to different investors. This article explains the key differences between growth and value stocks to help you make smart investing decisions.
What are Growth stocks?
Growth stocks belong to companies which are expected to increase revenues and earnings faster than the market average. These companies typically reinvest profits to fuel more expansion and innovation instead of paying dividends to shareholders. You’ll find growth stocks in dynamic sectors like technology, biotech, and e-commerce that have potential for disruptive growth.
When comparing growth stocks to Value stocks, it’s necessary to learn their major differences. Growth stocks usually have higher price-to-earnings (P/E) ratios because investors are ready to pay premiums for future growth potential. However, this also makes them more volatile and sensitive to investor sentiment.
Characteristics of Growth Stocks
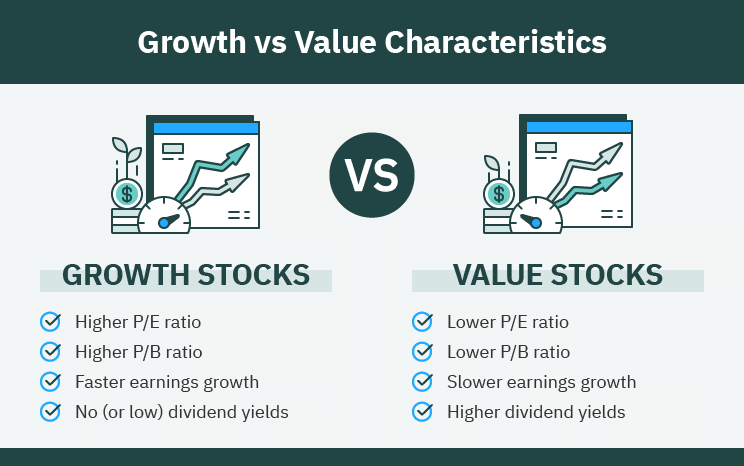
Growth stocks have a number of unique traits which set them apart from other stock types. These companies often have high growth potential for revenue and earnings, frequently surpassing market averages. As a result, growth stocks tend to have higher valuations as shown in their price-to-earnings (P/E) ratios versus overall market.
Another growth stock trait is higher volatility due to the high expectations placed on their future performance. You’ll often find these stocks in innovative technology industries where rapid advancements and market disruption are common. Investing in growth stocks generally requires long-term vision as short-term fluctuations can be more extreme.
Advantages of Growth Stocks
- Potential for major capital appreciation over time as company value rises
- Benefits from investing in market advancing, disruptive companies capitalizing on emerging trends
- Attractive for investors not seeking dividends and prioritizing long-term growth
- Chance to invest in innovative companies with strong competitive edge and loyal customers
- Possible market outperformance and substantial returns if company delivers high growth
What are Value Stocks

Unlike growth stocks, value stocks represent companies that are currently undervalued by the market. Their stocks trade at prices lower than fundamentals suggest they should, letting investors buy them at a discount.
Value stocks represent companies whose stocks are trading at lesser price as compared to their fundamentals like earnings, cash flows, assets and other intrinsics. The market has inflated the value of these stocks, often due to temporary setbacks, negative views or an out-of-favor industry.
Value investors believe intrinsic value will eventually get recognized, leading to share price appreciation. Unlike growth stocks, value stocks often have stable earnings and cash flows and pay dividends.
Comparing growth vs value stocks shows value stocks typically have lower price-to-earnings (P/E) and price-to-book (P/B) ratios, signaling they are undervalued relative to peers. You’ll often find value stocks in mature industries which are considered less risky.
Characteristics of Value Stocks
Comparing growth vs value stocks shows value stocks have distinct traits:
- Low price-to-earnings (P/E) and price-to-book (P/B) ratios, signaling undervaluation versus peers
- High dividend yields since companies distribute significant earnings to shareholders
- Stable earnings and cash flows, reflecting mature business models and established market spots
- Potential for value appreciation if market recognizes undervaluation
- Often in mature or out-of-favor cyclical industries with investors
- Considered less risky than growth stocks because of their stable fundamentals and lower valuations
Advantages of Value Stoc
When comparing growth vs value stocks, value stocks offer key advantages such as:
- Potential for steady returns and price increases if true company value gets recognized
- Lower risk as a result of stable fundamentals, undervaluation and mature industries
- Attractive for investors seeking income via relatively high dividend yields
- Chance to purchase discounted stocks compared to intrinsic value
- Tend to be less volatile and offer more stability versus growth stocks
Performance Comparison Between Growth and Value stocks
Growth stocks historically outperform value stocks in bull markets and economic booms. Growth companies capitalize on favorable conditions to increase revenue and earnings expansion, fueling share price rises.
On the other hand, value stocks tend to perform better during bear markets and recessions. Investors often shift focus to undervalued companies with strong fundamentals and stable cash flows in challenging times – value stock assets.
Over long timeframes, numerous studies show value investing outperforms growth investing. While growth stocks can temporarily overtake, value stocks tend to deliver superior long-run returns due to inherent undervaluation and appreciation potential.
Interest rates, inflation and industry trends also impact relative growth vs value performance. As a result, diversification between both investment styles is strongly recommended.
Key Differences: Growth vs Value Stocks
Below table covers differences between growth and value stocks that every investor should know:
| Trait | Growth Stocks | Value Stocks |
|---|---|---|
| Price | Overvalued | Undervalued |
| Earnings | High growth | Low P/E |
| Risk | High | Relatively low |
| Dividends | Low or none | High yields |
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Growth and Value Stocks:
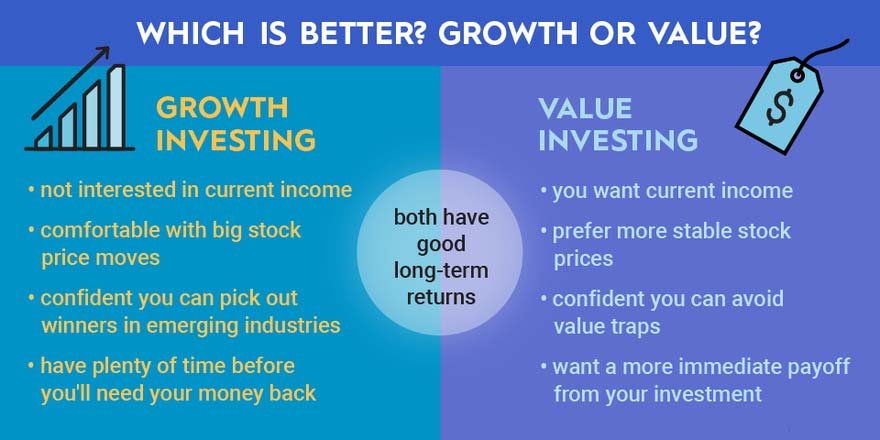
When deciding between growth and value stocks, consider factors that align with your investment goals:
- Financial aims: Growth stock suits long-term appreciation goals, while value stock provides steady dividend income.
- Timeframe: Growth stocks need longer timelines to realize full potential, whereas value stocks can deliver shorter-term returns.
- Risk appetite: Growth stocks tend to be more volatile due to higher valuations, while value stocks are generally less risky due to lower valuations and stable fundamentals.
- Income needs: Value stocks typically pay higher dividends, attracting income-seeking investors. Growth stocks focus on profit reinvestment over dividends.
Carefully weighing these aspects helps investors determine if a growth or value investing decision, or a combination of them, meets their financial objectives and risk preferences.
Diversification and Combining Growth and Value Stocks
Owning both growth and value stocks can diversify portfolio risk and returns. Growth stocks provide significant appreciation potential. While value stocks hedge risk with lower valuations and dividends.
Key benefits when combining both types, include:
- Reducing volatility by balancing growth risk with stable value stocks
- Capturing upside in different market environments when each style outperforms
- Supporting different goals with growth appreciation and value income
Investors can diversify more within each group by picking varied sector and industry stocks.
How to Identify Growth and Value Stocks

When comparing growth and value stocks, investors can use some basic metrics and ratios to identify growth and value stocks:
- Price-Earnings (P/E) ratio – Growth stocks tend to have higher P/Es, while value stocks have lower P/Es.
- Price-Book (P/B) ratio – Value stocks usually have lower P/Bs, meaning they are undervalued relative to book value.
- Earnings growth Companies with higher expected earnings growth are often seen as growth stocks.
- Return on Equity (ROE) and Return on Capital Employed (ROCE) – Value stocks often have higher ROEs and ROCEs, showing efficient use of capital.
Analysis of business model, competitive edge and industry trends is also crucial for spotting both growth and value stocks.
Investing Strategies

When comparing growth vs value stocks, investors can employ different strategies based on goals and risk appetite.
Strategies for investing in growth stocks:
- Focus on companies with strong long-term growth potential and ability to lead markets
- Analyze industry trends, competitive advantages and innovation to identify disruptive companies
- Prepare for higher volatility and have long-term horizon to ride out market swings
Strategies for investing in value stocks:
- Look for undervalued companies with strong fundamentals, steady earnings and healthy cash flows
- Do thorough fundamental analysis to identify stocks trading below intrinsic value
- Consider out-of-favor industries or companies facing temporary issues
- Prioritize stocks with attractive dividend yields for potential income
Remember, balancing growth and value stocks can help manage overall risk and returns.
Factors that Affect Growth and Value Stocks

When comparing growth and value stocks, performance depends on various factors like current state of economy, interest rates, industry trends and company related factors:
- Economic health and market cycles: Growth stocks tend to beat value stocks in bull markets and when economy grows. Value stocks often do better in bear markets and recessions.
- Rates and inflation: Higher rates and inflation can impact growth stocks more. Value stocks may handle it better due to lower valuations.
- Industry shifts: Growth stocks in innovative or disruptive spaces can ride hot trends, while value stocks may struggle from changes in mature sectors.
- Company specifics: Management quality, competitive edge and company fundamentals play huge role in both growth and value stocks.
Conclusion
Bottom line is when comparing growth vs value stocks, it’s critical that you understand their main differences and match your investing strategy to your financial goals and risk appetite.
Growth stocks offer big growth potential but also mean more volatility. Value stocks provide steadier returns, dividends and lower risk as they are undervalued. Balancing growth and value give portfolio stability.
While growth and value stocks are the main types, there are other types that can provide huge returns like penny stocks. Penny stocks are low-priced shares in small companies that have huge potential but can be risky bets.